Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the thyroid gland, which is located at the base of your neck. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and weight. Although thyroid cancer is not as common as other types of cancer, its incidence has been increasing over the years. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a favorable prognosis.
What is Thyroid Cancer?
Thyroid cancer develops when cells in the thyroid gland grow uncontrollably and form a tumor. It can be categorized into several types:
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer: The most common type, accounting for about 80% of all thyroid cancer cases.
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer: The second most common type, representing around 10-15% of cases.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Less common, comprising about 4% of cases and can be hereditary.
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: A rare and aggressive form, making up about 2% of cases.
Causes of Thyroid Cancer
While the exact cause of thyroid cancer is unknown, several factors can increase the risk:
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited genetic mutations can predispose individuals to thyroid cancer.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation, especially during childhood, can increase the risk.
- Family History: A family history of thyroid cancer or other thyroid conditions can elevate the risk.
- Gender and Age: Thyroid cancer is more common in women and often occurs in people over 30.
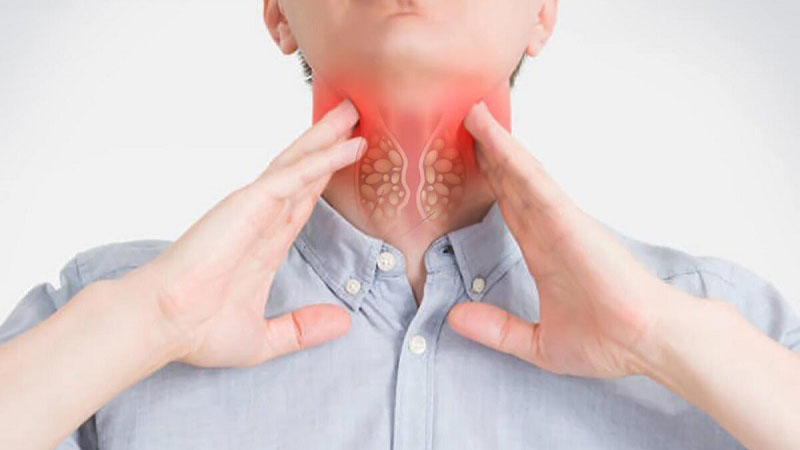
Diagnosis and Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer: Early-stage thyroid cancer might not cause any symptoms. As the cancer grows, it may cause:
- A lump or swelling in the neck
- Pain in the neck and throat
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Difficulty swallowing
- Persistent cough not related to a cold
Methods of Diagnosing Thyroid Cancer: Diagnosing thyroid cancer involves a series of tests and evaluations
- Physical Examination: A doctor will check for lumps or nodules in the neck.
- Blood Tests: These tests measure levels of thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to assess thyroid function.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs can help visualize the thyroid and identify any abnormal growths.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: A small sample of thyroid tissue is removed using a fine needle and examined for cancerous cells.
- Radioiodine Scan: This test involves swallowing a small amount of radioactive iodine to detect thyroid cancer cells.
Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Treatment Methods for Thyroid Cancer: The treatment for thyroid cancer depends on the type and stage of cancer:
- Surgery: The most common treatment for thyroid cancer, involving the removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). Lymph nodes in the neck may also be removed if cancer has spread.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Used to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells after surgery. It involves swallowing radioactive iodine, which is absorbed by thyroid cells.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy beams to target and kill cancer cells. This is less common and used when surgery is not an option.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells, typically used for more aggressive types of thyroid cancer that do not respond to other treatments.
- Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs to target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth. This treatment is often used for advanced thyroid cancer.
Choosing the Appropriate Treatment Method: The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including
- Type and stage of thyroid cancer
- Age and overall health of the patient
- Presence of metastasis (cancer spread to other parts of the body)
- Patient preferences and potential side effects
Post-Treatment Care and Prevention of Thyroid Cancer
Care After Thyroid Cancer Treatment: Post-treatment care is essential for monitoring and maintaining health:
- Regular Follow-Ups: Periodic blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels and imaging tests to check for recurrence.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: If the entire thyroid is removed, patients will need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress can support overall well-being.
Measures to Prevent Thyroid Cancer: While it’s not always possible to prevent thyroid cancer, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Avoid Excessive Radiation Exposure: Limit exposure to unnecessary medical radiation, especially in children.
- Genetic Testing: For those with a family history of thyroid cancer, genetic counseling and testing can be beneficial.
- Regular Screening: People with high risk should have regular thyroid screenings to detect any abnormalities early.
Treatment of Thyroid Tumors with Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Effectiveness and Advantages
Thyroid cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. Early detection and appropriate treatment significantly improve the prognosis. If you notice any symptoms like a lump in your neck, hoarseness, or difficulty swallowing, seek medical advice immediately.
In Vietnam, if you need assistance or consultation regarding thyroid cancer, you can contact Dr. Phạm Anh Tú, a leading specialist in thyroid disorders. Do not hesitate to seek medical advice or call the hotline if you have any concerns about your thyroid health. Taking proactive steps towards diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and ensure better thyroid health.
